English Name: Rosemary Extract
Botanical Source: Extracted from the leaves of Rosmarinus officinalis, an aromatic evergreen shrub.
Specification
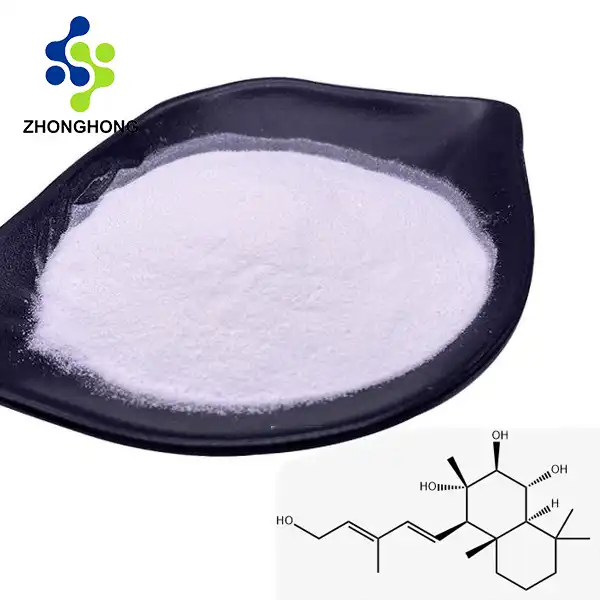
Active Ingredient: Rosemary contains multiple active components. Commonly, the content of carnosic acid and carnosol combined is ≥ [X]% (HPLC-tested), typically around 20% - 60% depending on extraction method and grade.
Purity: High, with minimal impurities, ensuring quality and efficacy.
Appearance
It usually presents as a greenish to brownish liquid or a dry powder. The liquid form has a characteristic herbal aroma, while the powder form is more convenient for certain applications.
CAS Number
For carnosic acid: 3650-09-7; for carnosol: 5957-80-2. These are the main active constituents, and the overall extract CAS can vary depending on composition.
Lead Time
Lead time: 3 - 7 Working Days. Minor adjustments might occur based on order quantity and production schedule.
Package
Packaging: 25kg/drum, with 27 drums/tray. Packaging materials are designed to protect the product from light, air, and moisture, maintaining its freshness and potency.
Main Market
Main Market: European, North America, Asia etc. It is widely used across these regions in various industries.
Applications
Health Supplements:
As a potent antioxidant, it helps combat oxidative stress, potentially protecting cells from damage. Some studies suggest it may support cardiovascular health and have anti-inflammatory effects, aligning with the antioxidant and potential metabolism-boosting aspects. While more research is needed for the cancer preventive claim, its antioxidant properties are promising.
Cosmetics:
In anti-aging creams, it can scavenge free radicals, reducing skin aging signs like wrinkles and fine lines. In skin-soothing lotions, its anti-inflammatory nature calms irritated skin, providing relief.
Food Industry:
It is a natural preservative, inhibiting the growth of spoilage microorganisms, and thus prolonging the shelf life of food products. Added to functional beverages, it imparts a pleasant herbal flavor while also offering health benefits.
Note: Specifications may vary, and it's advisable to consult for customization.
Effect and Function
Rosemary extract has the effects of strengthening the skin barrier and deeply moisturizing the skin. Its anti-inflammatory properties also help soothe irritated or sensitive skin. In addition, its role in antibacterial, anticancer and other aspects has been fully confirmed.
application
Rosemary extract has strong antioxidant, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, anti-aging and other effects, and is widely used in food, cosmetics, medicine and other fields.
Maximum allowable use amount and maximum allowable residue standard for food additives
The Chinese name of the additive allows the use of the Chinese name of the food containing the additive. The maximum allowable usage amount (g/kg) and the maximum allowable residual amount (g/kg) of the additive function
Rosemary extract fried food antioxidant 0.3
Rosemary extract fermented meat product antioxidant 0.3
Rosemary extract, meat enema antioxidant 0.3
Rosemary extract Western style ham (smoked, smoked, steamed ham) antioxidant 0.3
Rosemary extract fried meat antioxidant 0.3
Rosemary extract is a 0.3% antioxidant for smoking, grilling, and grilling
Rosemary extract sauce braised meat products antioxidant 0.3
Rosemary extract pre made meat product antioxidant 0.3
Rosemary extract animal fats (lard, butter, fish oil, and other animal fats) antioxidant 0.3
Rosemary extract, plant oil antioxidant 0.7
chemical property
Yellowish brown powder or brown paste, liquid. There is a special aroma. Heat resistance (stable at 200 ℃), good UV resistance, and effective prevention of oil oxidation. Better antioxidant capacity than BHT. It is usually sold in formulations with vitamin E and other ingredients, and has a synergistic effect. Generally, its antioxidant capacity increases with the increase of its dosage, but at high concentrations, it can cause oil to precipitate and discolor water containing foods. Insoluble in water, soluble in ethanol and oil.
Purpose:
antioxidant. Suitable for low-fat foods such as meat products, mayonnaise, seasonings, fried foods, etc. The general dosage in Japan is 500mg/kg.
Production method
Firstly, the scope of use and added standards should be determined according to local regulations.
In use, antioxidants can be used alone or in combination. Citric acid, ascorbic acid, and corresponding esters are often used as synergists with antioxidants to fully utilize the synergistic effects between different antioxidants and between antioxidants and synergists, making antioxidants more effective. In oils and fats, antioxidants should be added as early as possible, ideally before the production of peroxides. Because in severely rancid oils, antioxidants are adsorbed by the already formed oxidation products, making it difficult to achieve the expected effect.
Pharmacological effects of rosemary antioxidant
1 . Antioxidant components
Rosemary extract is a mixture of a series of substances with antioxidant activity extracted from the rosemary plant. The quality indicators of rosemary extract produced in industry are mainly measured based on the content of active ingredients, and the drafting of industry standards for rosemary extract in China is also underway.
Domestic and foreign literature data indicate that the antioxidant components in rosemary extract are mainly terpenes, phenols, and acids. The study also found that the antioxidant active ingredients and efficacy of rosemary vary under different environmental conditions and growth stages. 27 compounds were isolated and 22 compounds were qualitatively identified from rosemary extract using HPLC method. Divided into three categories: 1) phenolic acids: vanillic acid, caffeic acid, ferulic acid, and rosmarinic acid; 2) Diterpenes: Salvianolol, Rosmarinaldehyde, Oxalic Acid, Methyl Oxalic Acid, Rosmarinol, Epirosmarinol, Epirosmarinol Methyl Ether, and Epirosmarinol Ethyl Ether; 3) Flavonoids: hesperetin, apigenin, naringenin, 4,7-dimethoxybaiyangsu, jixin, 4,5,7,8-tetrahydroxyflavone, plantain glycoside, 6-hydroxyluteolin-7-glucoside, etc. The results of antioxidant experiments indicate that extracts with high activity typically contain the following 8 compounds: salvianolic acid, rosmarinic acid, oxalic acid, caffeic acid, rosmarinol, rosmarinaldehyde, naringenin, and lutein. Wang Wenzhong reported that salvianolic acid, rosmarinol, and rosmarinic aldehyde are the main antioxidant active ingredients, and the difference in their antioxidant efficacy is related to the amount of free radicals captured. Chen Meiyun believes that the oil soluble and highly efficient antioxidant substances in rosemary are bisphenol diterpenes, with salvianolic acid, oxalic acid, rosmarinol, and ursolic acid being the main active ingredients. Dong Wenbin et al. believe that there are more than 12 known antioxidant chemical components, including terpenes, flavonoids, and rosmarinic acid. Among them, the main component of terpenes is diterpenoid phenols, as well as rosmarinol, salvianolic acid, and some derivatives.
Almela et al. studied the antioxidant activity of rosemary extracts from different raw materials (wild, cultivated, and by-products of essential oil extraction) and found that the two strongest antioxidant substances, rosmarinic acid and carnitine, were most affected by the raw materials, drying, and distillation processes. The antioxidant activity of wild fresh grass extracts was comparable to that of pure delta vitamin E.
The antioxidant mechanism of rosemary extract
Due to the presence of multiple antioxidant active ingredients and various antioxidant mechanisms, rosemary has high and extensive antioxidant activity. At present, it is widely believed that the antioxidant mechanism of rosemary mainly lies in its ability to quench singlet oxygen, eliminate free radicals, cut off the chain reaction of lipid auto oxidation, and synergistically enhance the chelation of metal ions and organic acids. The reducing components in rosmarinic acid, such as phenolic hydroxyl groups, unsaturated double bonds, and acids, have antioxidant effects when present alone and synergistic effects when combined together.
Han Hongxing et al. established a mouse model of exercise-induced oxidative damage and found that the diterpenoid phenolic compounds in rosemary antioxidant extract have an impact on the endogenous oxidative system, which is the material basis of antioxidant activity. Wang Wenzhong et al. found from the structural analysis of active ingredients in rosemary that they have a catechol (the main active ingredient of tea polyphenol antioxidants) structural skeleton, which theoretically confirms the antioxidant activity and better stability of these ingredients. The study by Del Bano MJ et al. showed that oxalic acid and salvianolic acid have very strong anti mutagenic activity in human lymphocytes before and after gamma ray therapy, and the results before and after treatment showed the existence of different radiation protection mechanisms. Singletary et al. found that salvianolic acid can effectively increase the activity of glutathione S-transferase and quinone reductase in rat liver; Effective production of consistent DMBA-DNA adducts and inhibition of DMBA induced rat tumors. Rosemary's diterpenoid phenols have a good protective effect on liver injury in mice, and their toxicity is very low, making them a new drug for liver protection and enzyme reduction. Salviol and rosemary phenol have strong inhibitory activity on the proliferation of breast cancer cells, and the inhibitory activity of salviol has good selectivity, which can be developed as a new inhibitor of breast cancer proliferation activity.
Research by Li Yueting et al. has shown that rosmarinic acid can significantly inhibit the proliferation of rat mesangial cells stimulated by serum or lipopolysaccharides in the concentration range of 5-25mg/L, and significantly inhibit the secretion of IL-1 β in mesangial cells induced by lipopolysaccharides in the concentration range of 1-25mg/L. Research by Shang Yanjun et al. has shown that rosmarinic acid significantly inhibits uric acid production and NBT coloration induced by superoxide ions, making it a competitive inhibitor of xanthine oxidase. Zou Noon et al. reported through in vivo experiments in rats that rosmarinic acid can inhibit venous thrombosis, suppress collagen induced platelet aggregation, and promote fibrinolysis activity. Tu Pengfei et al. described in their article the role of rosmarinic acid in inhibiting thrombosis and immune regulation abroad. Li Weiguang et al. summarized the anti-inflammatory activity, antioxidant activity, immunosuppressive activity, and other pharmacological effects of rosmarinic acid, such as anti thrombosis, anti nephritis, anti HIV, anti depression, anti pneumonia, antibacterial, etc.
Ursolic acid belongs to the triterpenoid class and has a wide range of biological effects. It has a significant stabilizing and cooling effect on the central nervous system; It has antibacterial activity against G+, G - bacteria, and yeast in vitro. In addition, it has the effect of anti diabetes, anti ulcer and reducing blood fat. In recent years, it has been found that ursolic acid not only has resistance to various carcinogens and carcinogens, but also has inhibitory effects on the growth of various tumor cells such as P-388 and L-1210 leukemia, and A-549 human lung cancer cells. Therefore, ursolic acid can also induce F9 teratoma cells to become endodermal cells and resist angiogenesis. Therefore, the anti-tumor activity of ursolic acid is increasingly attracting people's attention.
3 Applications of Rosemary
Rosemary extract has shown great potential in the field of medicine. Traditional Chinese medicine believes that rosemary has a warm and pungent nature, with aromatic and stomach nourishing properties, as well as calming and calming effects. It is commonly used to treat various headaches, neurasthenia, and other conditions. Rosemary can also regulate blood pressure, reduce capillary permeability, and restore low blood pressure to normal (but its high irritability is not suitable for people with hypertension and epilepsy). Rosemary has strong anti-corrosion and antibacterial effects, and has a strong inhibitory and killing effect on Escherichia coli, Vibrio cholerae, and other bacteria. In medicine, the antioxidant properties of rosemary can also prevent DNA from being damaged by oxidation and reduce the occurrence of cancer. The study by Sharabani H et al. showed for the first time that the combination of plant polyphenol extracts (such as oxalic acid, the main polyphenol component of rosemary) and vitamin D derivatives can not only induce the isolation of leukemia cells in vitro, but also have anti leukemia activity in vivo. As early as 1983, European countries had developed drugs using rosemary extract to treat varicose veins, hemorrhoids, eczema, psoriasis, and skin infections. At present, the German company Nattermann has marketed rosmarinic acid as an antipyretic, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory drug. The latest research has shown that certain components of rosemary have the potential to become a drug source for treating myocardial infarction and anti-cancer and anti AIDS diseases. Inhaling the volatile components of rosemary extract can significantly inhibit allergic respiratory inflammation caused by indoor dust particles.
In summary, rosemary and its extracts have excellent antioxidant and antibacterial effects, and have a very broad application prospect in medicine, making them a valuable plant medicine resource.
The rosemary industry has developed into a mature industrial chain internationally!
1. Rosemary is a must-have seasoning for foreign families.
2. International high-end cosmetics and perfume additives.
3. The EU food safety regulation enforces standards for natural antioxidants.
4. International natural antibiotics!
5. Rosemary is evergreen all year round, blooming and fragrant. Long flowering cycle! Essential for various festivals.
6. Rosemary is a natural perfume bottle with fragrance throughout the year.
The international name for rosemary is RoseMary: the rose of the Virgin Mary! At present, the national implementation standards in our country have also been introduced, and the antioxidants of Chaoyang Industry and rosemary will enter thousands of households, dining tables, food, and oils! It is an efficient, stable, high-temperature resistant, and pollution-free preservative, and also has health food properties. It is already a mandatory standard in the European Union and has been used domestically. However, the current planting volume in China is just beginning, and the development in 50 years will not be saturated! Because the products produced from rosemary are essential consumer goods! It's natural and pollution-free again! Meet people's health needs! The domestic demand for planting area of 10 million acres is necessary to meet the demand for food and oil antioxidants! Currently, there are less than 120000 acres of cultivation in China!
_1728976869676.webp)