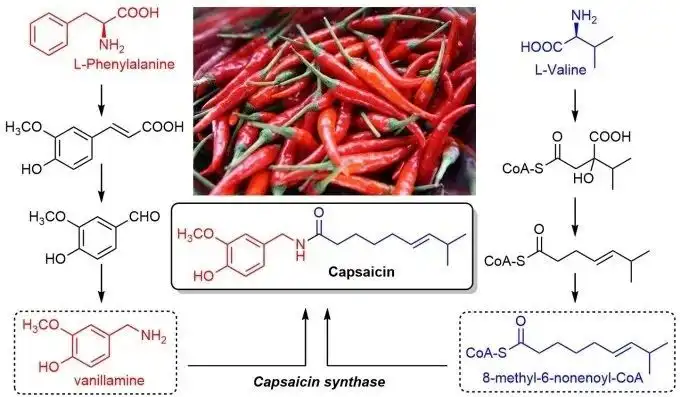
Chinese synonym Lorivide; N-nonanoic acid vanillide [=capsaicin (synthetic)]; Chili monocarboxylic acid; N-Nonoyl Vanillin; Capsaicin (synthetic); 94 capsaicin; Capsaicin, capsaicin (synthetic); Capsaicin (synthetic), 97%
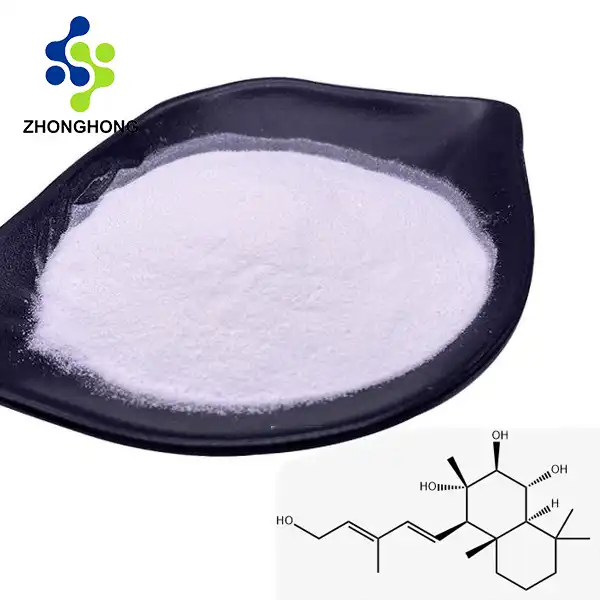
English name Nonivamide
The English synonym Nonivamide (Synthetic Capsaicin); N-((Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl)4-nonanamide; N-Nonanoyl vanillylamide; Nonanamide, N-((4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)meth; SYNTHETIC CAPSAICIN; PELARGONYL VANILLYLAMIDE; PELARGONIC ACID VANILLYLAMIDE; N-PELARGONIC ACID VANILLYLAMIDE
CAS number 2444-46-4
Molecular formula C17H27NO3
Molecular weight 293.4
EINECS number 219-484-1
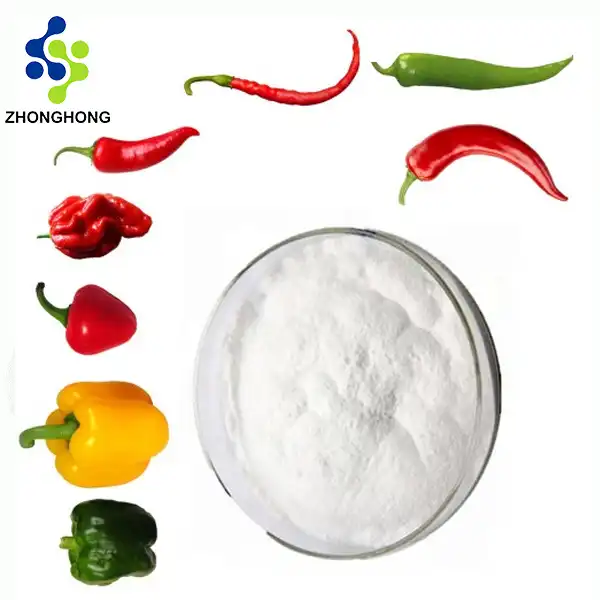
Nonivamide Extract: Benefits, Uses, and Supplier Guide
1. What is Nonivamide?
Product Source
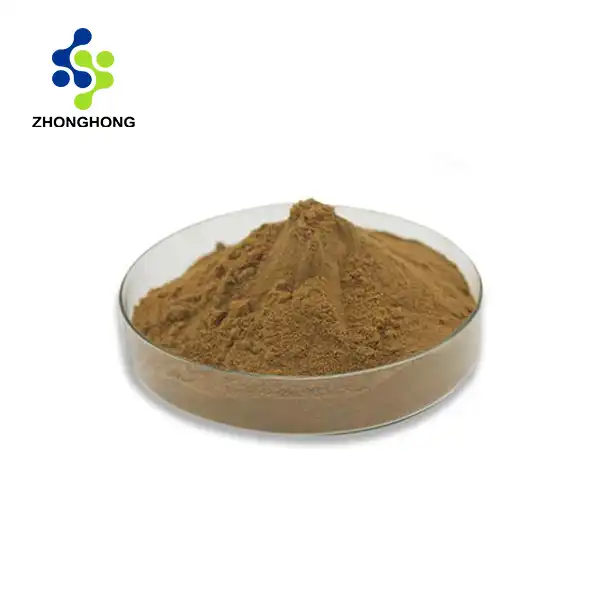
Nonivamide, a capsaicinoid compound, is derived from natural chili peppers (genus Capsicum). Shaanxi Zhonghong Investment Technology Co., Ltd., a leading high-tech enterprise, specializes in extracting and purifying nonivamide using advanced technologies to ensure ultra-high purity (>99%) and bioavailability.
Extraction Method
Supercritical CO2 Extraction: Preserves bioactive compounds without solvents.
Chromatographic Purification: Utilizes HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography) for precision.
2. Health Benefits of Nonivamide
Nonivamide is renowned for its physiological effects:
Pain Relief: Binds to TRPV1 receptors, alleviating muscle and joint discomfort.
Anti-Inflammatory: Reduces inflammation in arthritis and neuropathy.
Metabolic Boost: Enhances thermogenesis for weight management.
Antioxidant Protection: Neutralizes free radicals linked to chronic diseases.
Targeted Benefits for Specific Groups:
Athletes: Accelerates post-workout recovery.
Chronic Pain Sufferers: Non-addictive alternative to opioids.
Skincare: Used in topical creams for enhanced blood circulation.
3. Product Specifications & Safety
Purity & Compliance
| Parameter | Standard | Testing Method |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | ≥99% | HPLC |
| Pesticide Residues | <0.01 ppm (EU Limit) | GC-MS |
| Heavy Metals | Lead <1 ppm, Arsenic <0.5 ppm | ICP-MS |
| Microbial Contaminants | Total Plate Count <100 CFU/g | USP <61> |
4. Applications & Usage
Primary Use Cases:
Pharmaceuticals: Pain-relief patches, neuropathy formulations.
Nutraceuticals: Weight-loss supplements, metabolic enhancers.
Cosmeceuticals: Anti-aging serums, cellulite-reduction creams.
Recommended Dosage:
Topical Use: 0.025–0.1% concentration in creams/gels.
Oral Supplements: 2–5 mg/day (consult a healthcare provider).
5. Quality Assurance & Certifications
Shaanxi Zhonghong’s nonivamide meets global standards:
ISO 9001:2015-certified manufacturing.
FDA/GMP Compliance: Audited production facilities.
Third-Party Testing: Reports available upon request.
Production Workflow:
Raw Material Sourcing → 2. Supercritical Extraction → 3. HPLC Purification → 4. Quality Testing → 5. Packaging.
6. Safety & Precautions
Avoid contact with eyes/mucous membranes.
Conduct a patch test for topical applications.
Contraindicated for pregnant women or individuals with cardiovascular issues.
7. Why Choose Shaanxi Zhonghong?
R&D Excellence: 20+ patents, partnerships with 5 top universities.
Global Reach: Supplies to 30+ countries, including Pfizer, Unilever, and BASF.
Custom Solutions: Tailored purity grades (90%–99.9%), bulk discounts, and OEM support.
8. Ordering & Logistics
MOQ: 1 kg (sample orders accepted).
Packaging: Sealed aluminum bags with desiccant.
Shipping: DHL/FedEx, 3–7 days worldwide delivery.
9. FAQ
Q: Is nonivamide safe for long-term use?
A: Yes, at recommended doses. Clinical studies show no significant adverse effects.
Q: Can you provide COA (Certificate of Analysis)?
A: Yes, each batch includes a COA verifying purity and safety.
Q: Do you offer private-label services?
A: Yes, custom formulations and branding available.
10. Contact for Quotes & Samples
📧 Email: liaodaohai@gmail.com
🌐 Buy Nonivamide, Capsaicinoid Supplier, Natural Pain Relief Extract
References:
USP-NF Guidelines on Botanical Extracts.
nonivamide extract, nonivamide benefits, pharmaceutical-grade capsaicinoid, natural pain relief supplier.
YOU MAY LIKE
_1728976869676.webp)