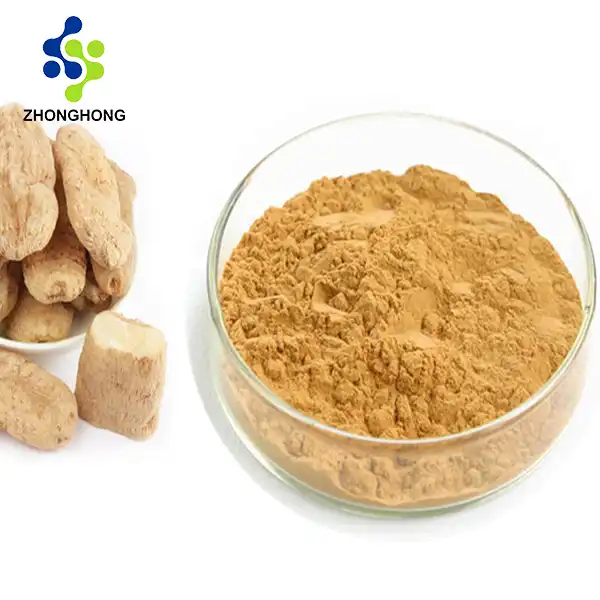
English Name: Gastrodia Rhizoma Extract
Botanical Source: Extracted from the rhizomes of Gastrodia elata Blume.
Specification
The specification “Bakuchiol ≥ 98% (HPLC)” is incorrect. For Gastrodia Rhizoma Extract, it should be relevant to its own active components, like Gastrodin ≥ [X]% (HPLC-tested), where the percentage depends on the quality grade, usually ranging from 5% - 20% or other appropriate values.
Purity: High, with strict control of impurities to meet pharmaceutical or food-grade standards.
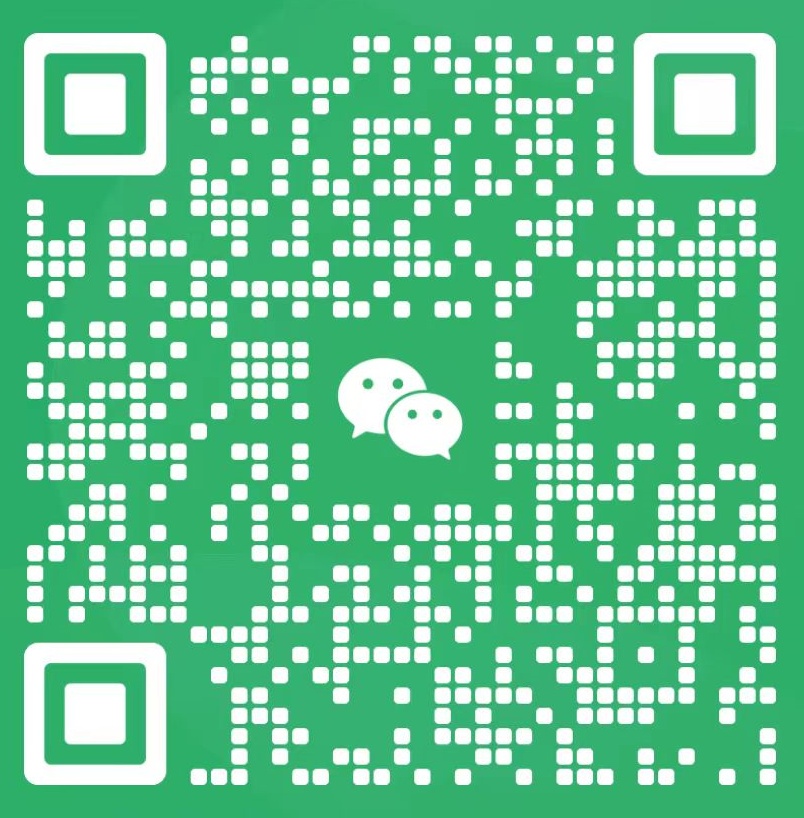
Appearance
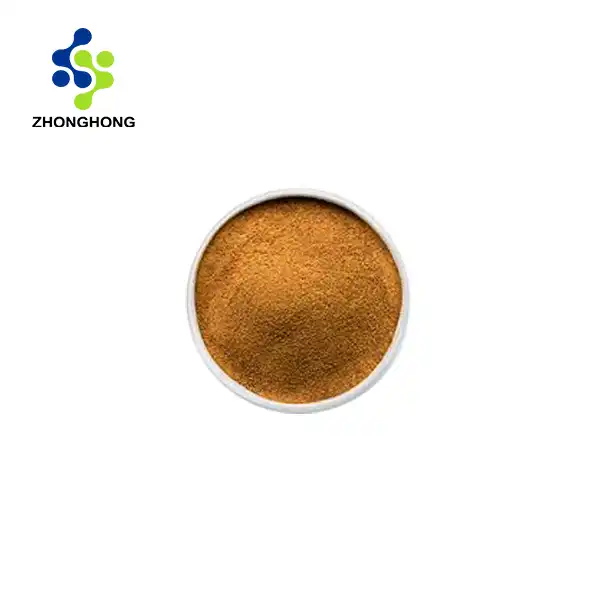
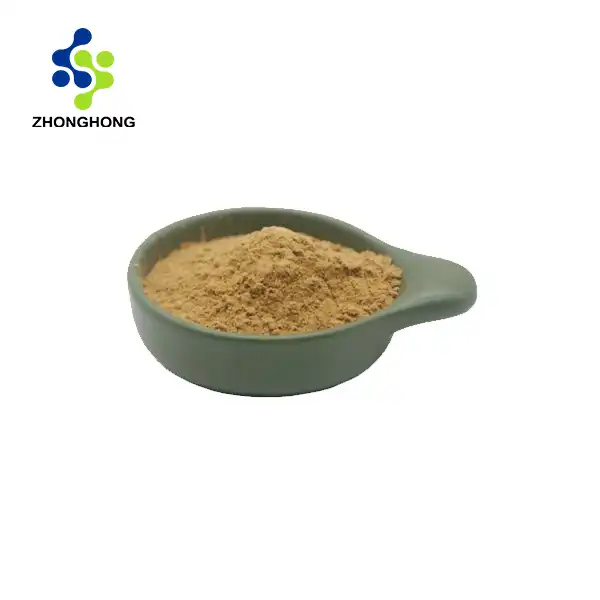
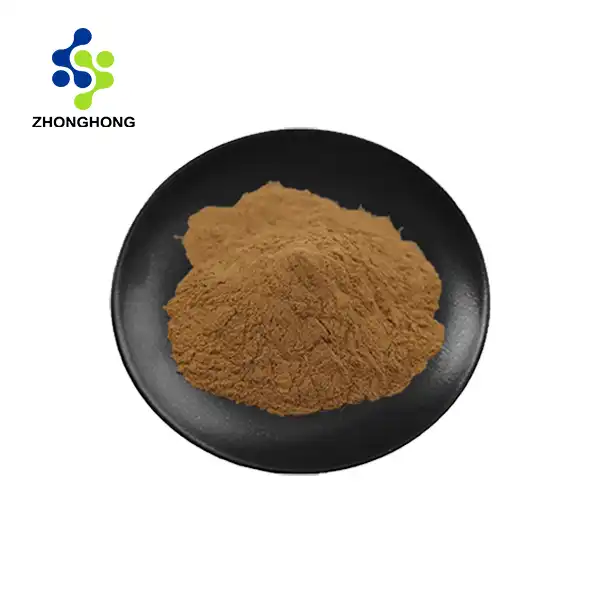
It generally presents as a light brown to brown powder, not the yellow oily liquid as wrongly indicated. The powdered form is more common due to extraction and drying processes.
Odor: Characteristic, faintly aromatic smell related to the plant source.
CAS Number
For Gastrodia Rhizoma Extract, while the whole extract may not have a single CAS, its main active ingredient Gastrodin has CAS NO. 62499-27-8.
Lead Time
Lead time: 3 - 7 Working Days. This may be adjusted depending on order quantity and production schedule, but generally, it ensures relatively prompt delivery.
Package
Packaging: 25kg/drum, with 27 drums/tray. The drums are made of suitable materials to maintain product stability, protect from moisture, light, and other environmental factors, ensuring the quality of the extract during storage and transportation.
Main Market
Main Market: European, North America, Asia etc. It has a wide range of applications and demands in these regions, being used in different industries.
Applications
Health Supplements:
Traditional uses suggest it helps with neurological health, such as relieving headaches and dizziness, rather than the provided “Antioxidant, metabolism booster, potential cancer preventive” which are not its typical primary functions. However, some recent studies explore its potential antioxidant properties.
It may also assist in improving sleep quality and reducing stress in some formulations.
Cosmetics:
In anti-aging creams, it could potentially contribute to skin firmness and elasticity improvement, leveraging its possible effects on promoting cell regeneration.
In skin-soothing lotions, it may help calm irritated skin, taking advantage of its natural soothing properties related to its traditional medicinal uses.
Food Industry:
It is not a typical natural preservative as stated. But in some specialized functional foods or beverages, it may be added in small amounts for its potential health benefits, like enhancing cognitive function, following strict regulatory approvals.
Premium Gastrodia Rhizoma Extract by Shaanxi Zhonghong Investment Technology Co., Ltd. – Neuroprotective Power, Purity, and Global Excellence
1. Introduction to Shaanxi Zhonghong Investment Technology Co., Ltd.
Shaanxi Zhonghong Investment Technology Co., Ltd. is a leading high-tech enterprise specializing in the extraction, purification, and application of bioactive plant compounds. With agile R&D capabilities, state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities, and a global distribution network spanning 30+ countries, we serve the pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and cosmetic industries. Our Gastrodia Rhizoma Extract embodies our dedication to quality, innovation, and sustainability, supported by advanced technology and partnerships with top-tier academic institutions.
2. Gastrodia Rhizoma Extract: Product Overview
Source & Extraction Method
Botanical Source: Gastrodia elata rhizomes (premium-grade, ethically sourced raw materials).
Extraction Method: Ultrasonic-assisted ethanol extraction combined with macroporous resin purification, achieving >98% bioactive compound retention.
Chemical Properties
Active Compounds: Gastrodin (≥5%), polysaccharides (≥20%), vanillyl alcohol.
Appearance: Light brown fine powder.
Solubility: Water-soluble and ethanol-soluble, ideal for capsules, tablets, and liquid formulations.
Health Benefits
Neuroprotection: Enhances cognitive function, reduces oxidative stress in the brain.
Anticonvulsant: Supports management of neurological disorders.
Anti-Inflammatory: Alleviates joint and muscle inflammation.
Cardiovascular Support: Regulates blood pressure and improves circulation.
Usage & Dosage
Dietary Supplements: 50–300 mg daily in capsules or tablets.
Pharmaceuticals: Used in formulations for epilepsy, migraines, and neurodegenerative diseases.
Cosmetics: Incorporate 0.2–1% in serums or creams for anti-aging and skin-soothing effects.
Precautions
Consult a healthcare professional before use if pregnant, nursing, or on medication.
Store in a cool, dry environment away from light and moisture.
3. Product Specifications & Safety Standards
| Parameter | Standard | Testing Method |
|---|---|---|
| Gastrodin Content | ≥5% | HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography) |
| Heavy Metals (Pb, As, Cd) | <1 ppm (total) | ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry) |
| Pesticide Residues | <0.01 ppm | GC-MS (Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry) |
| Microbial Limits | Total Plate Count <1000 CFU/g | USP <61> |
4. Production Process (Image-Supported Workflow)
Raw Material Selection: High-quality Gastrodia rhizomes subjected to rigorous quality checks.
Extraction: Ultrasonic-assisted ethanol extraction for optimal bioactive yield.
Purification: Macroporous resin and column chromatography to isolate gastrodin and polysaccharides.
Drying: Low-temperature spray drying to preserve stability.
Quality Control: Validated via HPLC, UV-Vis spectroscopy, and microbial testing.
(Include an infographic detailing these steps)
5. Applications Across Industries
Pharmaceuticals: Formulations for epilepsy, Alzheimer’s, and Parkinson’s disease.
Nutraceuticals: Cognitive-enhancing supplements and stress-relief capsules.
Cosmetics: Anti-aging creams, redness-reduction serums, and scalp care products.
Functional Foods: Added to brain-health beverages or energy bars.
6. Quality Assurance & Certifications
Equipment: HPLC, ICP-MS, GC-MS, and advanced spectroscopic systems.
Certifications: ISO 9001, FDA, GMP, Halal/Kosher, and Organic certifications (EU/USDA).
Traceability: Batch-specific certificates of analysis (CoA) with QR code tracking.
7. Why Choose Zhonghong’s Gastrodia Rhizoma Extract?
Global Logistics: Fast, reliable shipping to Asia, Europe, and the Americas.
Custom Solutions: Tailored concentrations and formulations for OEM/ODM partnerships.
Technical Support: Free samples, formulation guidance, and regulatory compliance assistance.
8. FAQ
Q: Is your extract suitable for vegan products?
A: Yes, it is 100% plant-based and free from animal-derived ingredients.
Q: Can this extract be used in injectable formulations?
A: Yes, our high-purity grade meets pharmacopeial standards for injectables.
Q: What is the shelf life?
A: 24 months when stored in airtight containers under recommended conditions.
Q: What is the MOQ?
A: MOQ starts at 1kg for samples; bulk orders are negotiable.
9. References & Scientific Backing
PubMed Study on Gastrodin’s Neuroprotective Effects
Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2020 Edition) Standards.
FDA GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe) Certification.
Gastrodia Rhizoma Extract supplier, neuroprotective supplements, organic herbal extracts, pharmaceutical-grade gastrodin, cognitive health ingredients.
Contact for Product Inquiries & Purchasing:
Email: liaodaohai@gmail.com
_1728976869676.webp)