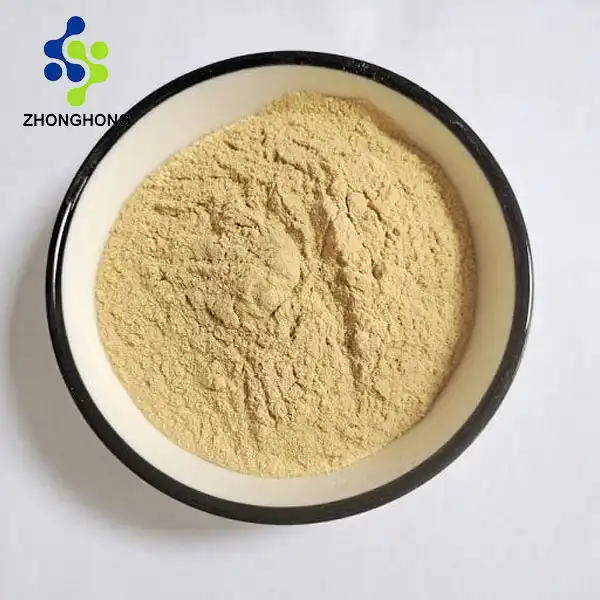
English name Soybean Extract
English synonyms Soybean Ext; SoyBean P.E; GlyciChemicalbooknemax (L.) Merr; Glycinemax (L.) merr. P.E; Soybean Extract
Purity: 98%
Packaging information: 1kg Remarks: API, pharmaceutical intermediates, fine chemicals
Clinical efficacy
Soy isoflavone extract can treat or prevent breast cancer, prostate cancer, osteoporosis, menopausal syndrome and other diseases, relieve menopausal symptoms, relieve hot flashes and vaginitis, prevent osteoporosis, hyperlipidemia, cardiovascular disease, etc.
Introduction to Soybean Extract
Company Profile: Shaanxi Zhonghong Investment Technology Co., Ltd. emerges as a leading force in the high-tech realm, seamlessly integrating agile research and development, joint innovation, integrated manufacturing, and global marketing. Dedicated to the domains of chemistry, materials, and life sciences, our focus zeroes in on the extraction, separation, purification, and market application of plant active ingredients. We source top-tier raw materials from across the globe, which serve as the bedrock for our extensive product line. This includes a diverse array of natural plant extracts, coveted cosmetic raw materials, vital healthcare and pharmaceutical ingredients, vivid natural plant pigments, and delicious natural plant sweeteners, all meticulously refined to meet the exacting standards of various industries.
Value and Services Offered
Customized Solutions: Understanding the unique demands of different sectors, we offer bespoke formulations of soybean extract. For pharmaceutical companies striving to develop novel drugs, we can fine-tune the concentration and purity of the extract to meet specific therapeutic requirements. Cosmetic brands seeking to incorporate natural ingredients for anti-aging or skin rejuvenation purposes can rely on our expertise to create custom blends. And for health supplement manufacturers, we design formulations that enhance the overall efficacy of their products.
Technical Support: Our team of experts, well-versed in the nuances of plant chemistry and application, stands ready to provide comprehensive technical consultations. From elucidating the complex chemical properties of soybean extract to advising on the most effective application methods, we cover all bases. This involves guiding customers on optimal dosage, suggesting compatible formulations, and exploring potential synergistic effects when combined with other ingredients.
Quality Assurance: Quality is the linchpin of our business. A stringent quality control system oversees every step of the production process. Starting from the careful selection and inspection of raw materials, through the various extraction, separation, and purification stages, to the final packaging, we conduct a series of rigorous tests. These include purity analysis, solubility tests, and microbiological assays, ensuring that only the highest quality soybean extract reaches the market.
Product Characteristics and Specifications
Product Source and Chemical Properties: Our soybean extract is derived from premium soybeans, carefully selected for their rich nutritional profile. Chemically, it contains a host of bioactive compounds, with isoflavones being a standout component. Isoflavones exhibit estrogen-like activity and play a crucial role in many of the extract's beneficial effects. The product description highlights its natural origin, purity level, and the presence of these key bioactive substances.
Benefits to Physical Health:
Heart Health Support: The isoflavones in soybean extract have been associated with cholesterol-lowering effects, particularly in reducing LDL cholesterol. This, in turn, can contribute to a decreased risk of heart disease. Additionally, it may help maintain healthy blood pressure levels, providing comprehensive cardiovascular support.
Menopausal Symptom Relief: For women navigating menopause, the estrogen-like activity of isoflavones can offer relief from hot flashes, night sweats, and mood swings. It presents a natural alternative to hormone replacement therapy, potentially reducing associated risks.
Bone Density Maintenance: Some studies suggest that soybean extract may have a positive impact on bone density. This is especially relevant for postmenopausal women, who are at a higher risk of osteoporosis, as it could potentially slow down bone loss.
Antioxidant Defense: Packed with antioxidants, the extract scavenges free radicals in the body, protecting cells from oxidative damage. This antioxidant activity is linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases such as cancer.
How to Consume:
Supplements: The most common form is capsules or tablets. The recommended dosage typically ranges from 50 mg to 150 mg per day, depending on individual needs and health goals. It's advisable to take them with a meal to enhance absorption and minimize potential stomach upset.
Incorporation into Food: Powdered soybean extract can be added to smoothies, yogurts, or baked goods. When doing so, it's crucial to adhere to the dosage instructions to ensure proper intake.
Precautions:
Dosage Caution: Exceeding the recommended dosage can lead to side effects. These may include gastrointestinal discomfort, hormonal imbalances in extreme cases, or allergic reactions. It's essential to start with the lowest effective dose and gradually increase if necessary, under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Interactions with Medications: If you are taking medications for heart conditions, thyroid disorders, or hormone therapies, consult your doctor before using soybean extract products. There is a potential for interactions that could alter the effectiveness of your medications or increase the risk of side effects.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Limited research exists regarding the safety of soybean extract during pregnancy and breastfeeding. As a precautionary measure, pregnant and breastfeeding women are advised to avoid using it without first consulting their obstetrician or pediatrician.
Product Specifications Table
| Project | Standard | Detection Method |
| Pesticide Residues | Below EU MRL limits | HPLC-MS/MS |
| Heavy Metals | <10 ppm (Pb, As, Cd, Hg) | ICP-MS |
Production Process (Visual Representation - Image Needed)
[Describe the production process in words. For example, high-quality soybeans are first carefully selected and cleaned to remove any impurities. Then, they undergo a solvent extraction process, often using ethanol or water, to draw out the active ingredients. This is followed by purification steps, such as chromatography, to separate and concentrate the desired compounds. Finally, the extract is dried to obtain the pure soybean extract. Insert a relevant image of the production flow chart or key steps here.]
Use Scenarios
Health Supplements: As a dietary supplement, soybean extract is highly sought after by those looking to bolster their heart health, manage menopausal symptoms, and boost their antioxidant defenses. It can be part of a daily health regimen for people of all ages, especially women in midlife.
Cosmetics: In the cosmetics industry, its antioxidant and skin-nourishing properties make it a valuable ingredient. It can be found in creams, lotions, and serums, helping to improve skin elasticity, reduce wrinkles, and protect against environmental damage.
Food and Beverage Industry: It can be incorporated into a variety of food and beverage products. For example, in soy milk, energy bars, or breakfast cereals, it adds nutritional value and potential health benefits.
Quality Control
From the initial inspection of raw materials to the final testing of the finished product, a strict quality control regime is in place. This ensures that every batch of soybean extract meets the highest standards. Only products that pass our rigorous quality checks are released to the market.
Product Details and Use Tutorial
The soybean extract product is carefully packaged to maintain its quality and potency. It comes in [packaging size and type], making it convenient for storage and use. Detailed instructions on how to use the product, including recommended dosages, mixing methods, and precautions, are provided on the product packaging and our website.
Transaction Feedback
Our customers' satisfaction is our top priority. Past customers have reported positive experiences, such as improved heart health, reduced menopausal symptoms, and better skin condition after using our soybean extract product. These testimonials serve as a testament to the effectiveness of the product.
Packaging, Tro
We use high-quality packaging materials to safeguard the product during shipping. Samples are available for customers who wish to test the product before making a large purchase. We offer a variety of delivery options and ensure timely shipping to meet our customers' needs.
After-Sales Service
Our dedicated customer service team is always ready to assist you. Whether you have questions about the product, its usage, or delivery, we will provide prompt and helpful responses.
General Information
This includes detailed product information, our company's rich history, and contact details. Customers can easily access this information to learn more about what we offer and how to get in touch.
Qualifications and Certifications
The company holds a host of relevant industry certifications, ensuring that our products meet international standards. These certifications [list relevant ones] are a testament to our commitment to quality and compliance.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) on soybean bioactive compounds.
Codex Alimentarius Commission standards for food additives and ingredients.
YOU MAY LIKE
_1728976869676.webp)