Comprehensive Guide to Shaanxi Zhonghong Tech’s Capsicum Red Pigment: Benefits, Quality, and Applications
1. Introduction to Shaanxi Zhonghong Investment Technology Co., Ltd.
Shaanxi Zhonghong Investment Technology Co., Ltd. is a globally renowned high-tech enterprise specializing in the extraction, purification, and application of plant-based bioactive compounds. With expertise in chemistry, materials science, and life sciences, the company delivers premium natural ingredients for industries such as food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and nutraceuticals. Their Capsicum Red Pigment, derived from Capsicum annuum (red chili peppers), exemplifies innovation, purity, and sustainability. Supported by 5 top-tier university partnerships, 20+ patented technologies, and a global compound library, Shaanxi Zhonghong sets industry benchmarks with purity standards 20% higher than competitors.
Core Strengths:
Scientific Leadership: Joint labs with 5 leading universities and 20+ patents.
Advanced Facilities: Equipped with HPLC, superconducting NMR, and precision detection systems.
Global Reach: Supplies tailored solutions to 30+ countries across Asia, Europe, and the Americas.
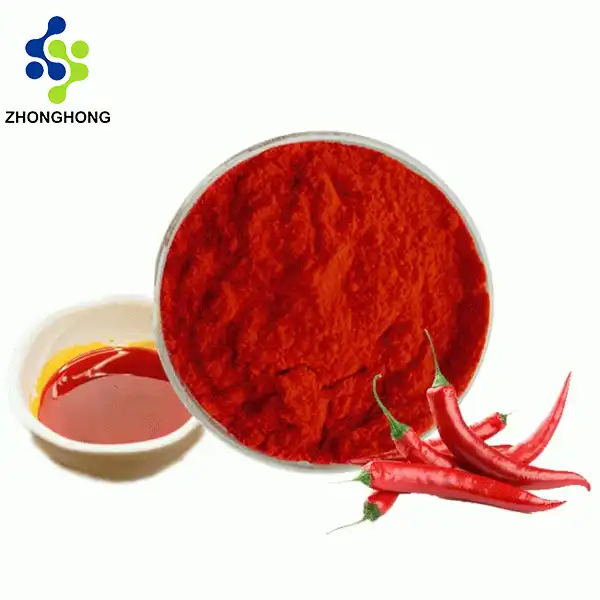
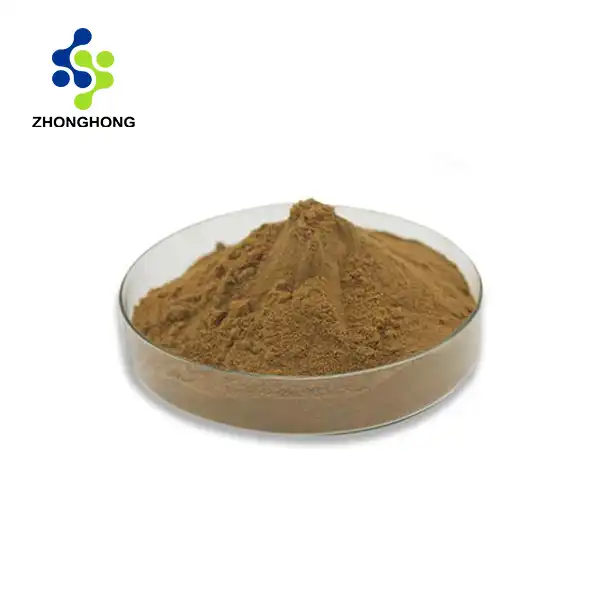
2. Product Overview: Capsicum Red Pigment
Source: Extracted from the fruits of Capsicum annuum, cultivated in pesticide-free farms.
Product Description:
A natural red pigment rich in carotenoids, primarily capsanthin and capsorubin.
Ideal for replacing synthetic dyes in food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.
3. Key Health Benefits
Antioxidant Properties: Neutralizes free radicals, reducing oxidative stress.
Anti-Inflammatory: Supports joint and cardiovascular health.
Eye Health: Contains lutein and zeaxanthin for retinal protection.
Metabolic Boost: May enhance thermogenesis and energy expenditure.
4. Usage Guidelines
Dosage: 0.1–1% in food/cosmetic formulations (varies by application).
Forms: Liquid extract, powder, or oil-soluble formulations.
Precautions: Avoid direct contact with eyes. Conduct patch tests for topical use.
5. Product Specifications & Quality Assurance
| Parameter | Standard | Detection Method |
|---|---|---|
| Pesticide Residues | Below EU MRL limits | HPLC-MS/MS |
| Heavy Metals | <10 ppm (Pb, As, Cd, Hg) | ICP-MS |
| Capsanthin Content | ≥5% (HPLC-verified) | HPLC-UV |
| Microbial Contaminants | Absence of pathogens | USP <61> Microbial Testing |
6. Extraction Method
Solvent Extraction: Ethanol or supercritical CO₂ for high carotenoid yield.
Purification: Chromatography to isolate capsanthin and remove impurities.
Standardization: Adjusted for color intensity (ASTA or CU units).
7. Applications & Target Audiences
Food Industry: Natural coloring for sauces, snacks, and beverages.
Cosmetics: Lipsticks, blushes, and skincare products.
Nutraceuticals: Antioxidant supplements for metabolic and eye health.
8. Quality Control & Certifications
GMP & ISO 9001: Compliant with global manufacturing standards.
Third-Party Testing: Independent validation for safety and purity.
Halal/Kosher: Certifications available upon request.
9. Packaging & Logistics
Options: 1 kg to 25 kg airtight, light-protected containers; customizable OEM/ODM packaging.
Shipping: Global air/sea freight; free samples available.
10. Why Choose Shaanxi Zhonghong?
Superior Purity: 20% higher capsanthin content via patented extraction.
Custom Solutions: Tailored formulations for specific color profiles.
Sustainability: Eco-friendly processes and ethical sourcing.
11. FAQ
Q1: Is Capsicum Red Pigment heat-stable?
A: Yes, stable up to 160°C, ideal for baked goods and processed foods.
Q2: Can it cause allergic reactions?
A: Rare; conduct patch tests for sensitive individuals.
Q3: Is it vegan-friendly?
A: Yes, 100% plant-derived and cruelty-free.
12. Contact for Inquiries & Orders
For technical specifications, COA, or bulk pricing, email liaodaohai@gmail.com.
13. References
National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) on capsanthin.
European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) guidelines on natural colorants.
Capsicum Red Pigment, Natural Food Colorant, Capsanthin, Antioxidant Dye, Bulk Chili Extract.
Partner with Shaanxi Zhonghong for vibrant, science-backed natural pigments!
Visual & Technical Enhancements
Production Infographic: Showcase steps from farming → extraction → quality control → packaging.
Certifications: Display ISO, GMP, Halal/Kosher logos.
CTA: “Request a Free Sample & Color Chart” linked to liaodaohai@gmail.com.
Transform your products with Shaanxi Zhonghong’s premium Capsicum Red Pigment – where nature meets brilliance! 🌶️🎨
YOU MAY LIKE
_1728976869676.webp)