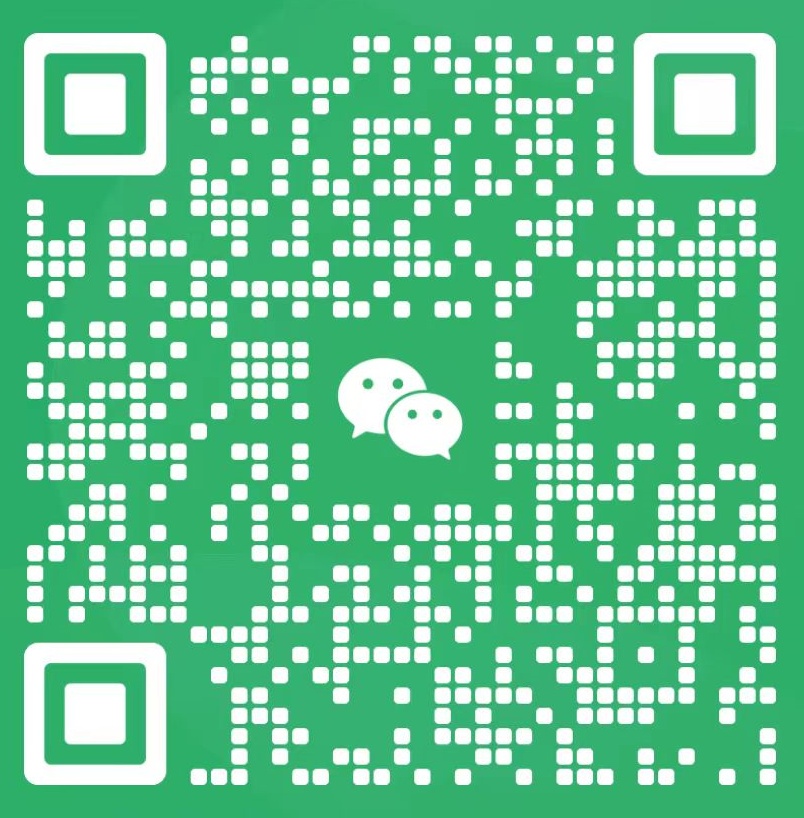
English name: Oat Straw Extract
Other names: Bromus, wild wheat
Product number: SC-006 COSMETIC
Product number: SC-011 HEALTH
Part of use: Wild oat fruit
Active ingredients: β-glucan, flavonoids
Product properties: Brown-yellow fine powder 100% through 80 mesh.
Specifications: β-glucan 20%-90%, 5:1, 10:1, 20:1,
Detection method: AOAC/TLC
Solubility: This product is easily soluble in water
Safe dosage: 3-5% Can be used with other active ingredients
1. Buckwheat Cellulose: The Ultimate Dietary Fiber Solution by Shaanxi Zhonghong Investment Technology
Introduction
Shaanxi Zhonghong Investment Technology Co., Ltd. is a pioneering high-tech enterprise specializing in the extraction, purification, and global distribution of premium plant-based ingredients. With expertise in chemistry, materials, and life sciences, the company leverages cutting-edge technology to produce Buckwheat Cellulose—a revolutionary dietary fiber derived from nutrient-rich buckwheat. Renowned for its sustainability, purity, and health benefits, this product is trusted by food, nutraceutical, and pharmaceutical industries worldwide.
2. Scientific Innovation & Global Leadership
Cutting-Edge R&D
Academic Partnerships: Collaborates with 5 top-tier universities to optimize extraction techniques and validate health benefits.
Proprietary Technology: 20+ patents and a proprietary global compound library ensure unmatched quality.
Advanced Equipment: Utilizes HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography) and CO2 supercritical extraction systems, achieving 99%+ purity and compliance with international standards.
Global Reach
Supplies tailored fiber solutions to food manufacturers, supplement brands, and pharmaceutical companies across 30+ countries in Asia, Europe, and the Americas.
3. Buckwheat Cellulose: Health Benefits & Applications
Health Benefits
Digestive Health: Promotes gut regularity, prevents constipation, and supports a healthy microbiome.
Blood Sugar Control: Slows glucose absorption, aiding in diabetes management.
Weight Management: Increases satiety, reducing calorie intake and supporting weight loss.
Cholesterol Reduction: Binds to bile acids, lowering LDL ("bad" cholesterol) levels.
Gluten-Free & Hypoallergenic: Ideal for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity.
Targeted Benefits for Specific Groups
Diabetics: Stabilizes post-meal blood sugar spikes.
Weight-Conscious Consumers: Enhances fullness and reduces cravings.
Elderly: Supports digestive and cardiovascular health.
4. Usage Guidelines & Safety
Applications
Food Industry: Added to baked goods, cereals, and beverages as a fiber enhancer.
Nutraceuticals: Capsules, tablets, or powders for dietary supplements.
Pharmaceuticals: Used as a binder or excipient in tablet formulations.
Recommended Dosage
Adults: 5–15 grams per day, gradually increased to avoid bloating.
Culinary Use: 2–5% of total recipe weight for fiber fortification.
Precautions
Drink plenty of water to prevent gastrointestinal discomfort.
Consult a healthcare provider if pregnant, nursing, or on medication.
5. Product Specifications & Quality Assurance
Chemical Profile
Purity: ≥95% cellulose content.
Safety & Compliance Standards
| Parameter | Standard | Testing Method |
|---|---|---|
| Pesticide Residues | ≤0.01 ppm (EU/EPA compliant) | GC-MS |
| Heavy Metals | Pb ≤1 ppm, As ≤0.5 ppm, Cd ≤0.2 ppm | ICP-MS |
| Microbial Limits | Total plate count ≤1000 CFU/g | ISO 4833-1:2013 |
| Moisture Content | ≤8% | Gravimetric Analysis |
6. Sustainable Production & Certifications
Eco-Friendly Process: CO2 supercritical extraction minimizes waste and energy consumption.
Certifications: ISO 9001, ISO 14001, Halal, Kosher, Non-GMO Project Verified, and FDA GRAS.
Custom Solutions: Adjustable particle size (50–200 mesh) and bulk packaging options.
7. Applications Across Industries
Functional Foods: Enhances fiber content in breads, pasta, and snacks.
Dietary Supplements: Key ingredient in prebiotic and weight management formulas.
Pharmaceuticals: Used as a stabilizer in tablet manufacturing.
8. Packaging, Logistics & Support
Packaging: Moisture-proof, food-grade bags (1 kg to 25 kg) or bulk containers.
Global Shipping: Fast delivery via DHL/FedEx with customizable logistics solutions.
Samples: Free samples available for quality evaluation.
9. Why Choose Shaanxi Zhonghong?
Innovation: 20+ patents and university-backed R&D for cutting-edge solutions.
Quality: Purity exceeds industry standards, verified by HPLC and microbial testing.
Trusted Globally: Partnered with leading brands in 30+ countries.
10. FAQs
Q1: Is buckwheat cellulose gluten-free?
Yes, it is naturally gluten-free and safe for celiac patients.
Q2: Can it be used in vegan products?
Absolutely—100% plant-based and cruelty-free.
Q3: What is the shelf life?
24 months when stored in a cool, dry environment (below 25°C).
11. Conclusion
Shaanxi Zhonghong’s Buckwheat Cellulose offers a versatile, science-backed dietary fiber solution for modern health needs. With rigorous quality controls, sustainable practices, and global certifications, it empowers businesses to create innovative, health-focused products that resonate with consumers worldwide.
References:
European Food Safety Authority (EFSA)
FDA Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS)
Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry (ACS Publications).
_1728976869676.webp)