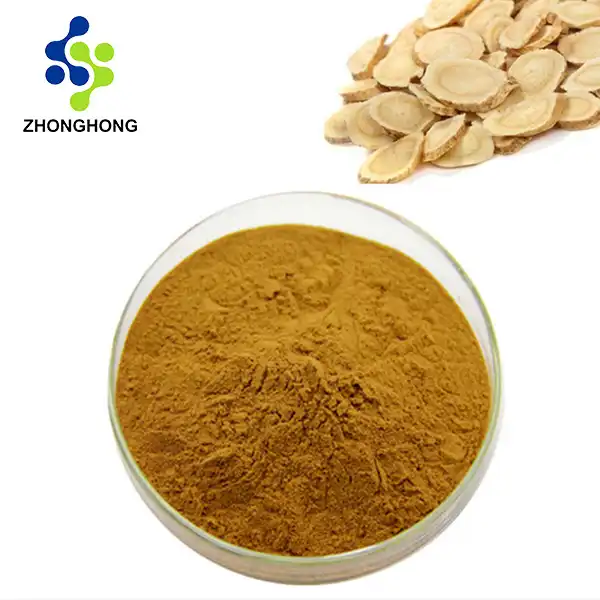
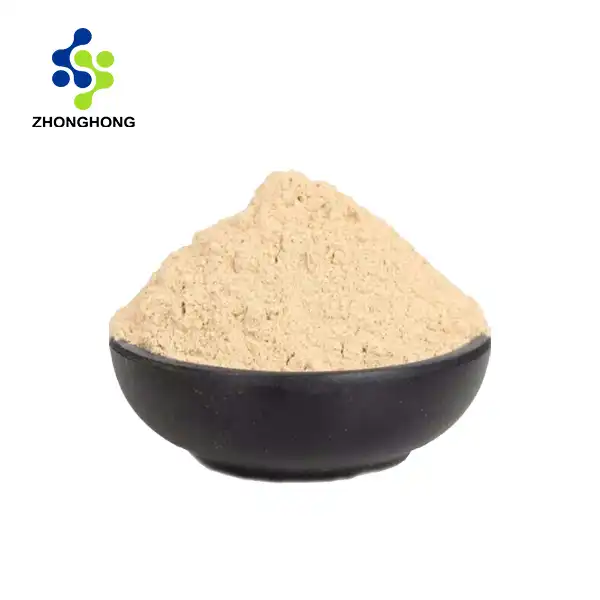
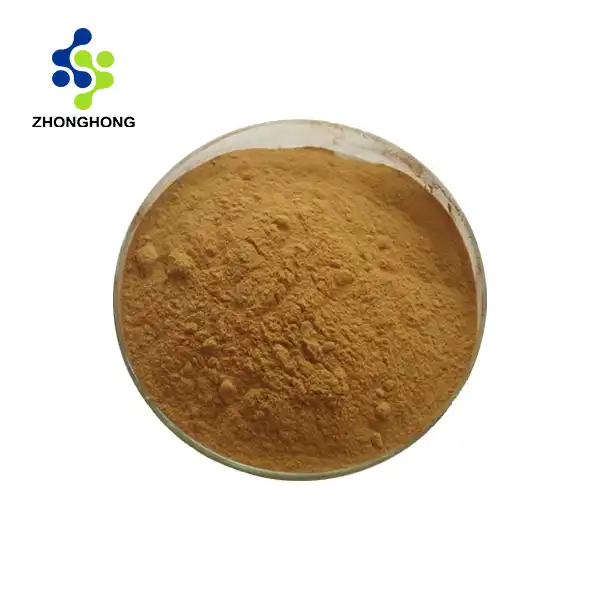
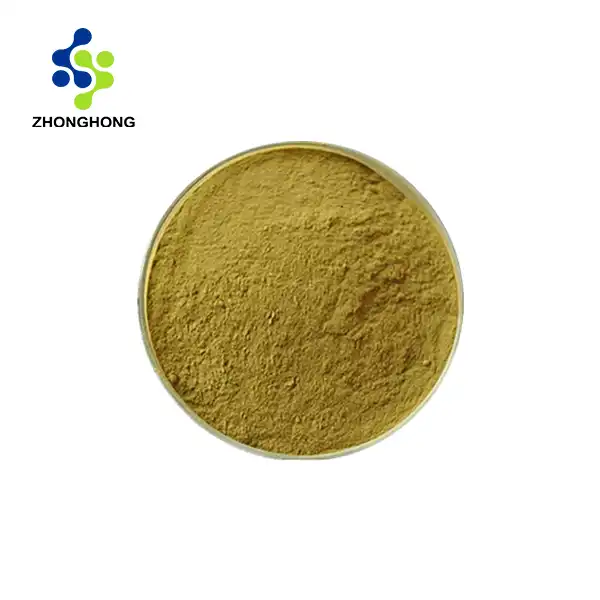
[Plant Latin name]: Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bge.
[Plant source]: It is the root extract of Mongolian Astragalus of the Leguminosae plant.
[Extraction process]: Dry the Astragalus root raw material, wash, dry, crush, add 10 times the amount of water, heat and boil for three times, 2 hours each time, combine the three extracts, concentrate and evaporate the water to an extract with a specific gravity of d=1.20, let it stand and cool, add ethanol to the extract and stir, let it stand and settle, centrifuge the precipitate, continue to add ethanol to the precipitate and stir, let it stand and centrifuge, get the crude Astragalus polysaccharide, remove the protein and mucus components with a mixed solvent, and get the pure Astragalus polysaccharide.
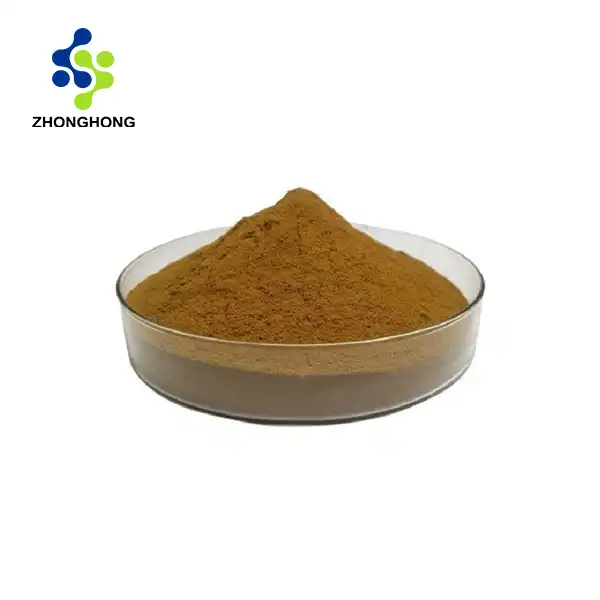
[Product properties]: This product is brown or gray white powder.
[Active ingredients]: Astragaloside IV, Astragalus polysaccharide
Product Overview
English Name: Astragalus Polysaccharide
Botanical Source: Extracted from the roots of Astragalus membranaceus.
Specification
Active Ingredient: Polysaccharides ≥ [X]% (HPLC-tested), typically ranging from 30% - 70% depending on extraction and purification processes.
Molecular Weight: Varies, generally in a certain range suitable for its bioactivity.
Appearance
It usually appears as a light yellow to brownish powder, which is water-soluble.
CAS Number
There is no single specific CAS number for Astragalus Polysaccharide as a whole due to its complex nature; different fractions or purified forms might have individual CAS numbers for their key components.
Lead Time
Lead time: 3 - 7 Working Days. Minor adjustments may occur based on production capacity and order volume.
Package
Packaging: 25kg/drum, with 27 drums/tray. Packaging materials are designed to protect the product from moisture and other contaminants.
Main Market
Main Market: European, North America, Asia etc. Applied in the fields of health supplements, pharmaceuticals, and functional foods.
Premium Astragalus Polysaccharide by Shaanxi Zhonghong Investment Technology Co., Ltd. – Immune Support, Purity, and Global Expertise
1. Introduction to Shaanxi Zhonghong Investment Technology Co., Ltd.
Shaanxi Zhonghong Investment Technology Co., Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise specializing in the extraction, purification, and application of plant-based bioactive compounds. With agile R&D, advanced manufacturing, and a global distribution network spanning 30+ countries, we serve industries such as pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, cosmetics, and food. Our Astragalus Polysaccharide exemplifies our commitment to quality, innovation, and sustainability, backed by cutting-edge technology and academic partnerships.
2. Astragalus Polysaccharide: Product Overview
Source & Extraction Method
Botanical Source: Astragalus membranaceus root (imported premium-grade raw materials).
Extraction Method: Advanced hot water extraction followed by ethanol precipitation, ultrafiltration, and lyophilization to ensure high polysaccharide content (>70%).
Chemical Properties
Active Compounds: Polysaccharides (≥70%), flavonoids, saponins.
Appearance: Fine white to off-white powder.
Solubility: Water-soluble, suitable for capsules, tablets, and liquid formulations.
Health Benefits
Immune Support: Enhances immune cell activity and antibody production.
Anti-Fatigue: Boosts energy metabolism and reduces oxidative stress.
Anti-Aging: Protects against cellular damage and supports skin health.
Cardiovascular Health: Regulates blood sugar and lipid levels.
Usage & Dosage
Dietary Supplements: 100–500 mg daily in capsules or tablets.
Functional Foods: Add to beverages, protein powders, or health bars.
Cosmetics: Incorporate 0.5–2% in serums or creams for anti-aging benefits.
Precautions
Consult a healthcare provider before use if pregnant, nursing, or on medication.
Store in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
3. Product Specifications & Safety Standards
| Parameter | Standard | Testing Method |
|---|---|---|
| Polysaccharide Content | ≥70% | Phenol-Sulfuric Acid Method |
| Heavy Metals (Pb, As, Cd, Hg) | <1 ppm (total) | ICP-MS |
| Pesticide Residues | <0.01 ppm | GC-MS |
| Microbial Limits | Total Plate Count <1000 CFU/g | USP <61> |
4. Production Process (Image-Supported Workflow)
Raw Material Selection: Ethically sourced Astragalus roots with strict quality checks.
Extraction: Optimized hot water extraction to preserve bioactive polysaccharides.
Purification: Multi-stage ultrafiltration and ethanol precipitation for high purity.
Drying: Lyophilization to maintain stability and solubility.
Quality Control: Rigorous testing via HPLC, UV-Vis, and microbial assays.
(Include infographic illustrating these steps)
5. Applications Across Industries
Nutraceuticals: Immune-boosting capsules, tablets, and gummies.
Pharmaceuticals: Adjuvant therapy for chronic diseases and recovery support.
Functional Foods: Fortified beverages, sports nutrition products.
Cosmetics: Anti-aging creams, serums, and masks.
6. Quality Assurance & Certifications
Equipment: HPLC, UV-Vis Spectrophotometer, ICP-MS, and GC-MS systems.
Certifications: ISO 9001, FDA, NSF, Halal/Kosher, and Organic (EU/USDA).
Traceability: Batch-specific certificates of analysis (CoA) and QR code tracking.
7. Why Choose Zhonghong’s Astragalus Polysaccharide?
Global Reach: Efficient logistics to Asia, Europe, and the Americas.
Customization: Tailor-made formulations for OEM/ODM clients.
Samples & Support: Free samples available; dedicated technical and regulatory guidance.
8. FAQ
Q: Is your Astragalus Polysaccharide organic-certified?
A: Yes, we offer both conventional and certified organic options.
Q: Can it be used in vegan products?
A: Absolutely. Our product is plant-based and free from animal-derived ingredients.
Q: What is the shelf life?
A: 24 months when stored in sealed containers under recommended conditions.
Q: What’s the MOQ?
A: MOQ starts at 1kg for samples; bulk orders are flexible.
9. References & Scientific Backing
PubMed Study on Astragalus Polysaccharide’s Immune Benefits
Chinese Pharmacopoeia Standards (2020 Edition).
FDA GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe) Certification.
Astragalus Polysaccharide supplier, immune-boosting supplements, organic plant extracts, pharmaceutical-grade polysaccharides, nutraceutical ingredients.
Contact for Product Inquiries & Purchasing:
Email: liaodaohai@gmail.com
_1728976869676.webp)